Configuring Servers
Manage MCP servers and tool availability.
Admins control which MCP servers and tools are available to the organization.
Adding a Server
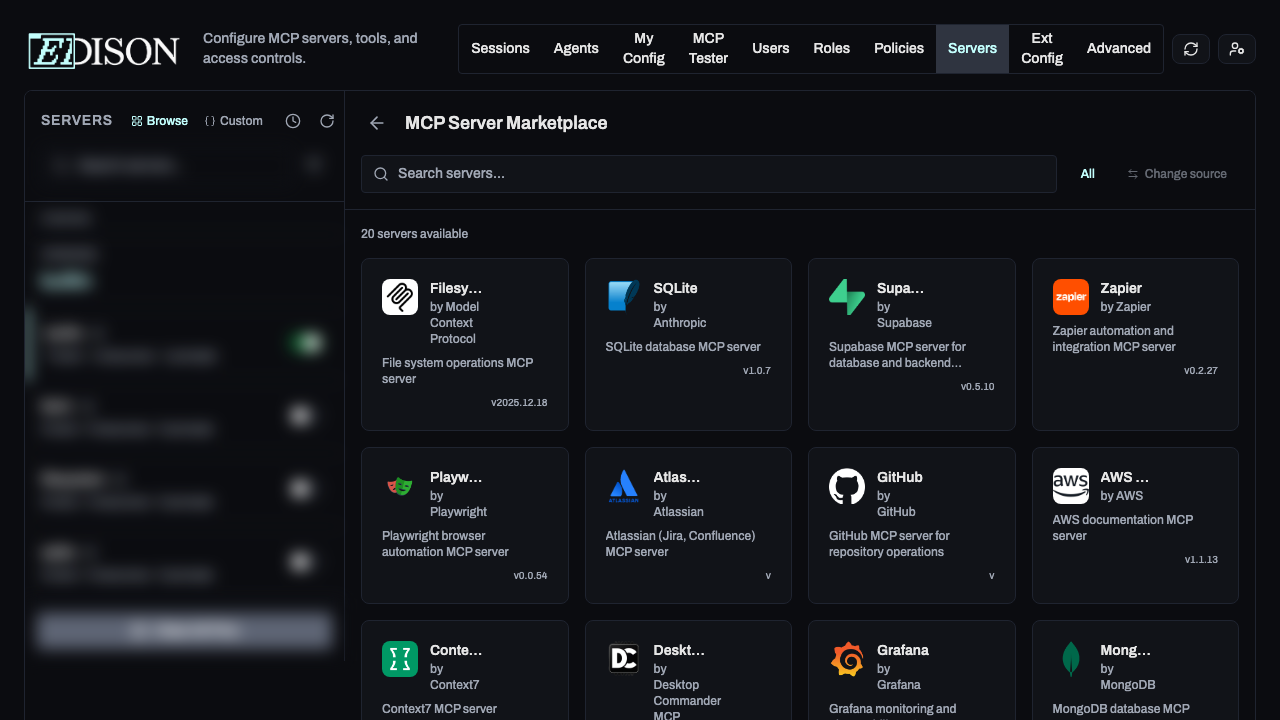
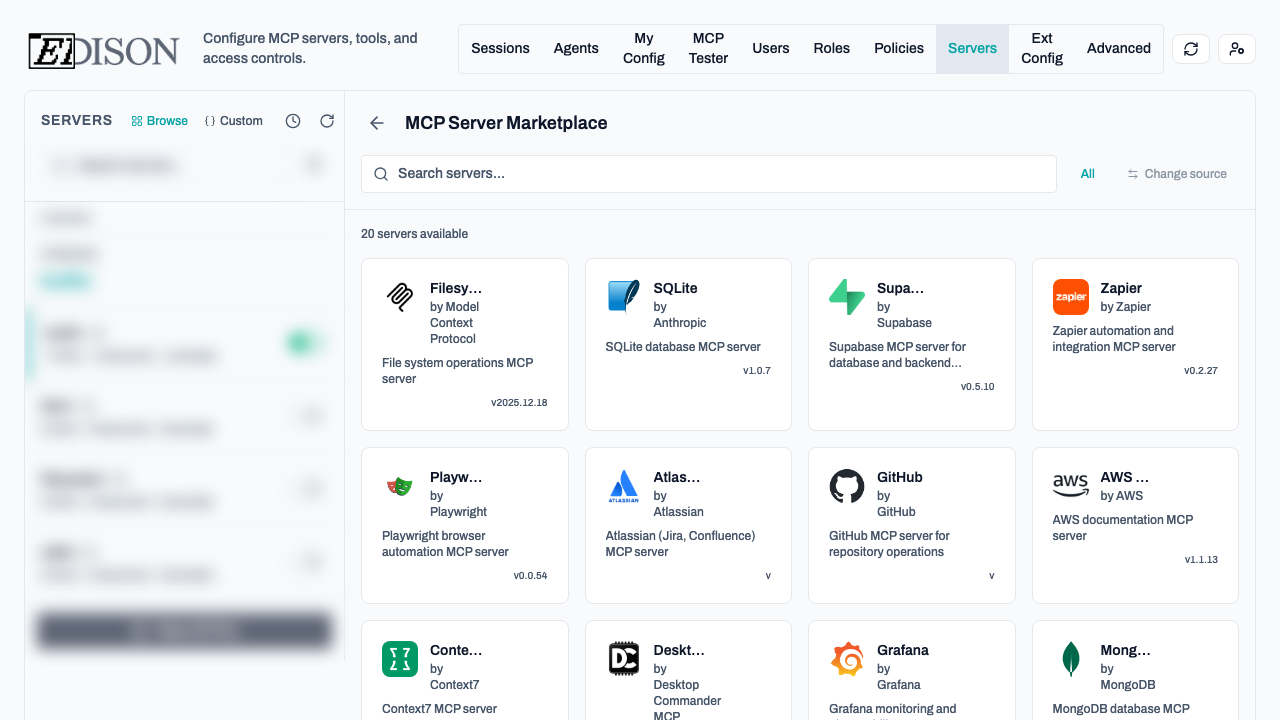
Option 1: Marketplace
- Click Browse Marketplace.
- Select a server and click Add.
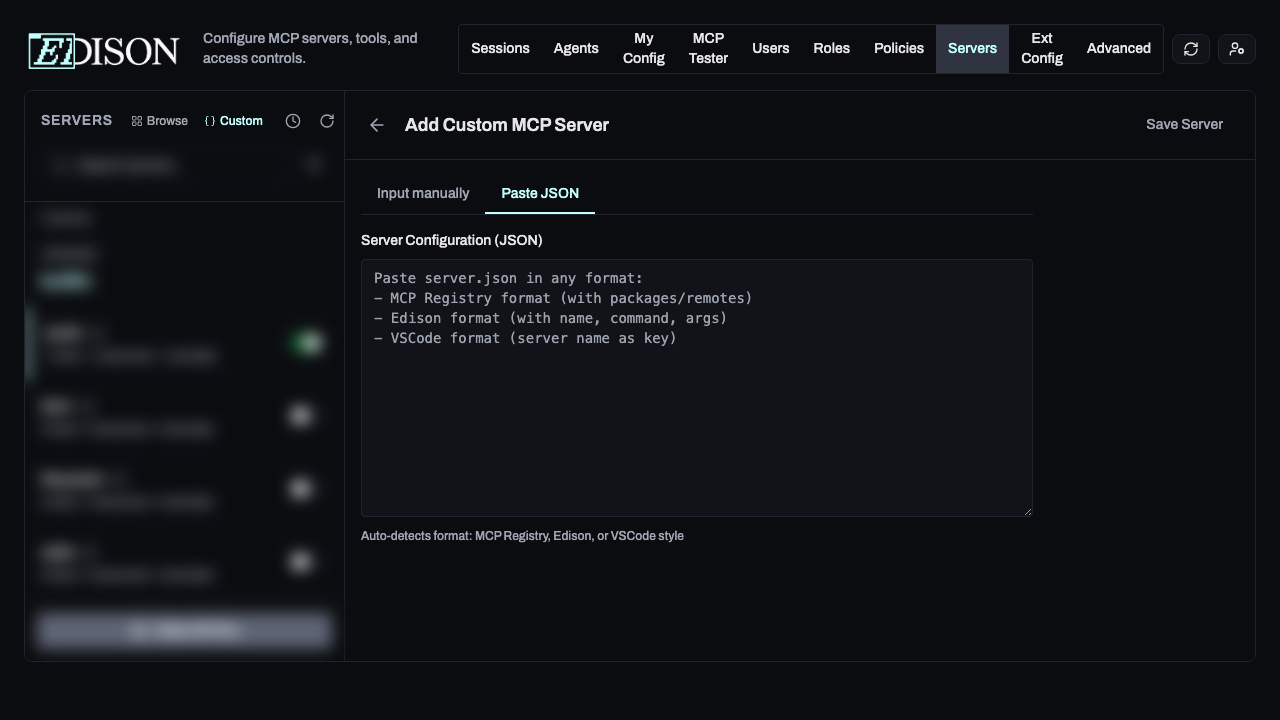
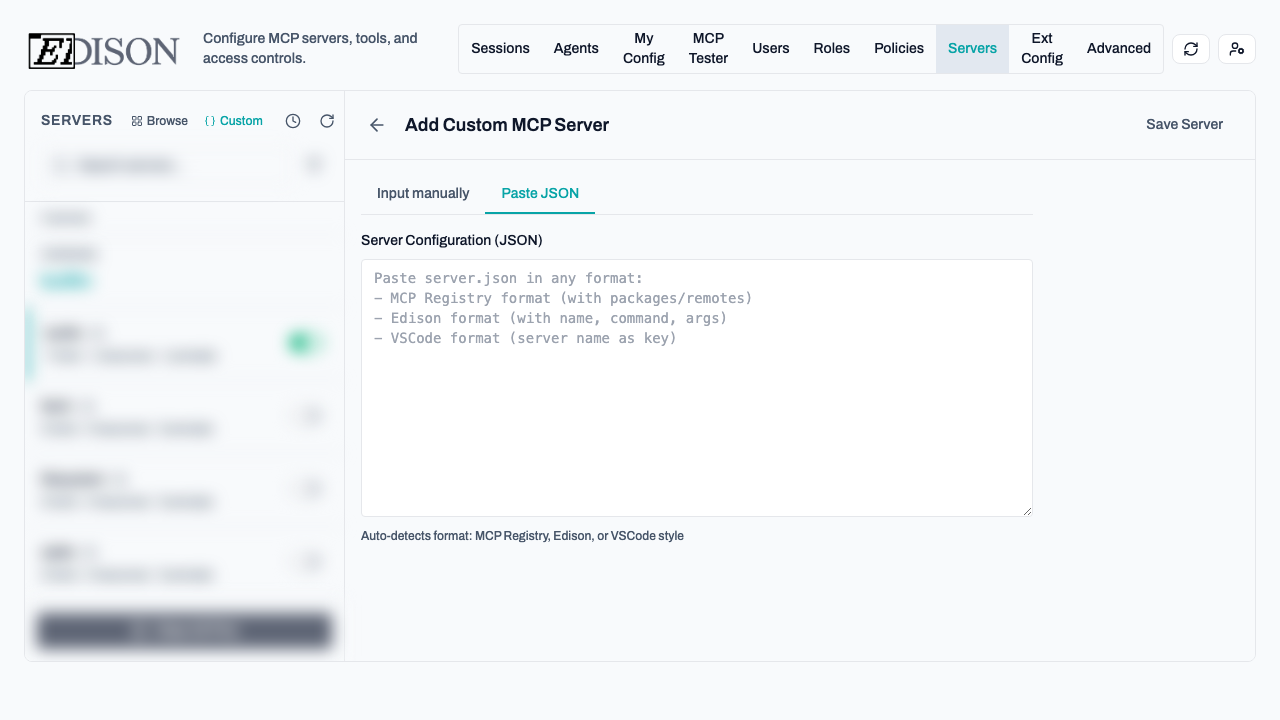
Option 2: Custom Server
- Click Add Custom.
- Manual: Enter the name, command (e.g.,
uvx,npx), and arguments. - JSON: Paste a configuration in VS Code or standard MCP format.
Template Variables
Use {VARIABLE_NAME} in arguments or environment variables. These can be configured globally by admins or individually by each user.
Server Management
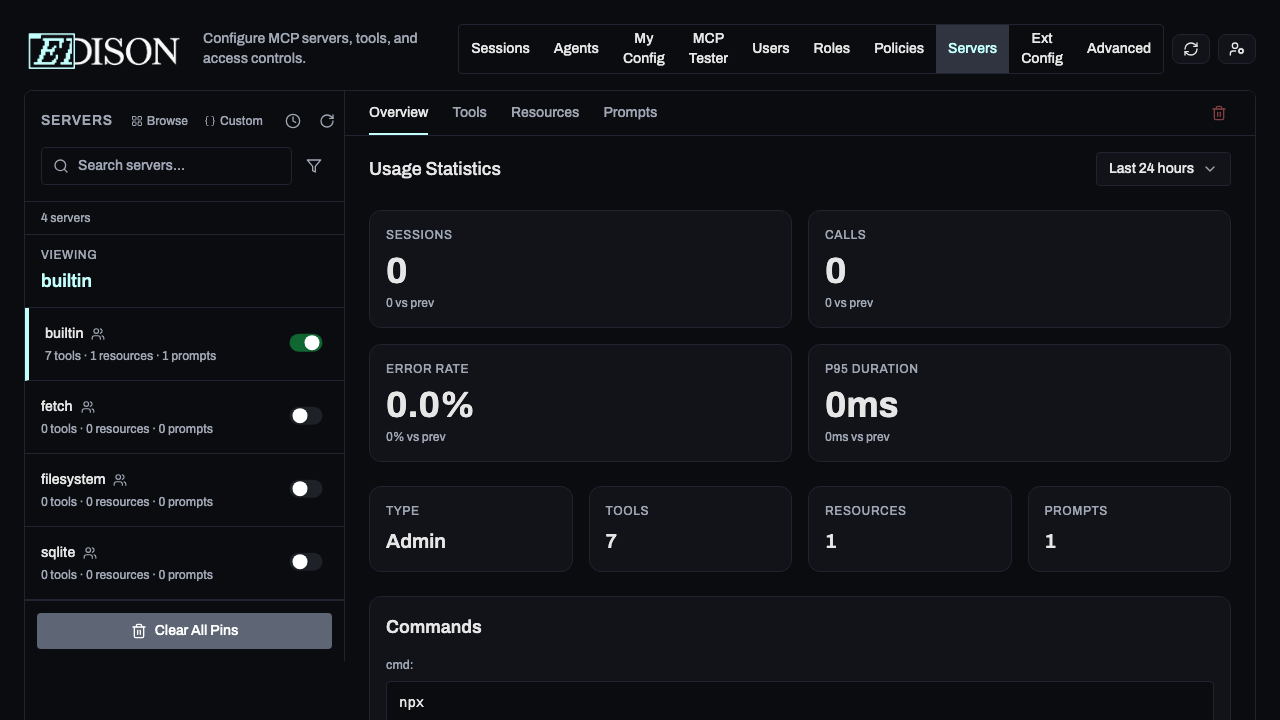
Overview
View the server's command, status, and detected capabilities (tools, resources, prompts).
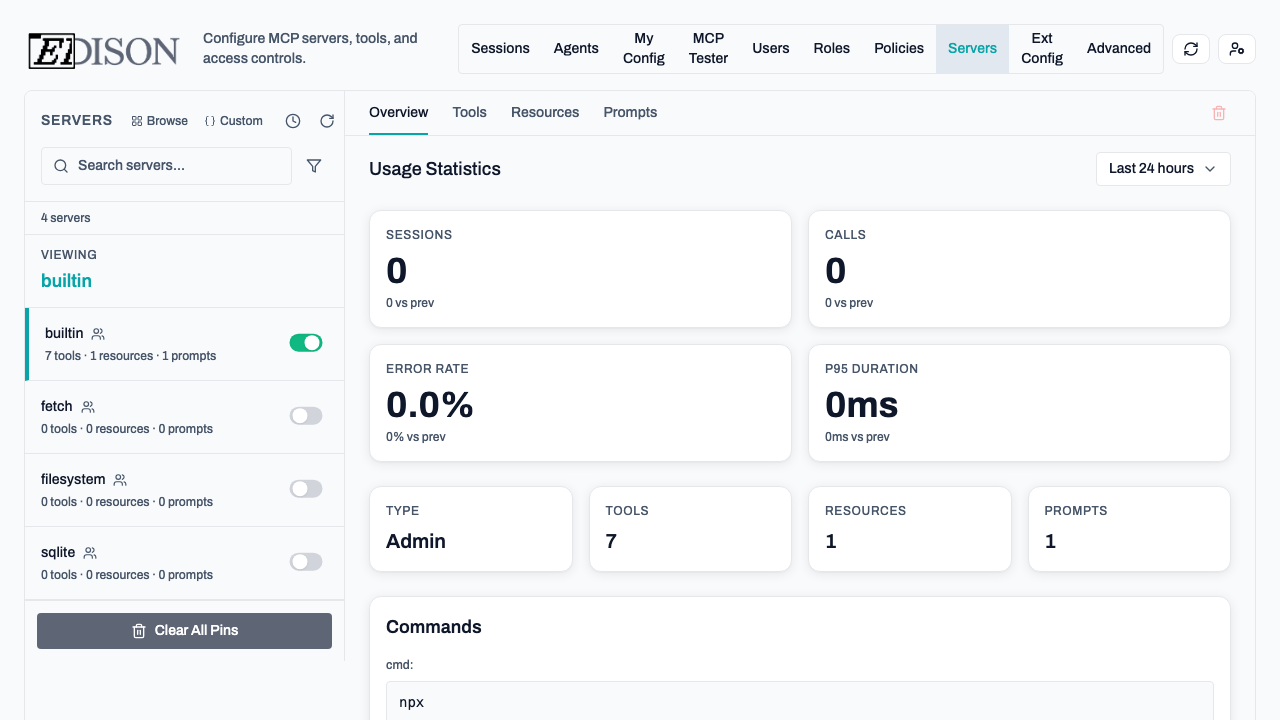
Status Toggles
- Enable/Disable: Turn servers on or off globally.
- Validate: Test the configuration. Edison Watch will attempt to start the server and discover its tools.
- Reinitialize: Restart all servers to apply configuration changes.
Tool Configuration
In the Tools tab, classify each tool:
- Enabled: Allow or block usage.
- Security Flags: Mark as Write Operation, Private Data, or Untrusted Data.
- ACL: Set the data sensitivity level.
Supply-Chain Security
Edison Watch automatically pins dependencies for servers that use package runners like npx or uvx. This prevents supply-chain attacks by locking exact package versions.
How Pinning Works
When a server is first mounted:
- Edison Watch resolves the full dependency tree (including transitive dependencies)
- Creates a lockfile (e.g.,
package-lock.jsonfor npm,uv.lockfor Python) - Stores the lockfile securely in the database
- Creates an ephemeral runtime environment from the locked dependencies
On subsequent mounts, the server uses the cached lockfile, ensuring identical dependency versions every time.
Pinning Status
In the server overview, you'll see:
- Pinned badge: Shows the package version that's locked (e.g.,
@modelcontextprotocol/[email protected]) - Pinned on [date]: When the dependencies were last locked

Clear Pin
Use the Clear Pin button to:
- Force re-pinning after updating a server's package version
- Resolve issues if a server misbehaves due to a corrupted pin
- Update dependencies when a new version is available

After clearing, the server will re-pin on the next mount. This may take 30-60 seconds on first run.
You can also clear all pins at once using the Clear All Pins button in the server list sidebar:
First Run: Servers using npx or uvx will take longer to start on first mount while dependencies are being pinned. This is a one-time process.
Interface Locking
Edison Watch monitors the interface (tools, prompts, and resources) that each MCP server exposes. This detects unexpected changes that could indicate a compromised or misconfigured server.
How Interface Locking Works
When a server is first mounted:
- Edison Watch discovers all tools, prompts, and resources the server exposes
- Records the complete metadata (names, descriptions, schemas) for each element
- Computes a cryptographic hash of this metadata
- Stores the "interface lock" in the database
On subsequent mounts, Edison Watch compares the current interface against the stored lock. Any differences are flagged as interface drift.
Types of Drift Detected
- New elements: A tool, prompt, or resource appears that wasn't there before
- Removed elements: A previously-seen element is missing
- Modified metadata: A description or schema has changed
Interface Drift Warning: When drift is detected, Edison Watch logs a warning and fires a security event. This helps you catch malicious updates or accidental misconfigurations.
Disabling Interface Locking
Interface locking is enabled by default for all servers. In some cases, you may want to disable it:
- Development servers that change frequently
- Servers with dynamically-generated tool lists
- Testing environments where drift is expected
To disable interface locking for a server:
Admin Only: Only administrators can enable or disable interface locking. This setting is per-server and persists across restarts.
Example Configurations
GitHub Integration

PostgreSQL Database

Zapier Automations

Local Filesystem

Active Sessions: Reinitializing servers may briefly interrupt active AI sessions.